What is Food Insecurity?

A food-insecure household means that members of the home don’t have access to enough healthy and nutritious food to support an active and healthy lifestyle. Homes that have low food security must often make tough choices about the amount and quality of food they are able to provide their families. Homes that are considered to have “very low” food security often miss meals.
Hunger In America
Even in the world’s greatest food-producing nation, children and adults face poverty and hunger in every county across America. In 2017:
- 40 million people struggle with hunger in the United States, including more than 12 million children.
- A household that is food insecure has limited or uncertain access to enough food to support a healthy life.
- Households with children were more likely to be food insecure than those without children
- 58% of food-insecure households participated in at least one of the major federal food assistance program — the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP, formerly Food Stamps); the National School Lunch Program and the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children (often called WIC)
Hunger In North Carolina
Every night, people in almost 630,000 North Carolina households don’t have enough to eat. North Carolina has the 8th highest rate of food insecurity in the nation.
- 1 in 6 people in southeast North Carolina are food insecure – 1 in 4 are children.
- 75% of North Carolina food bank clients have had to choose between paying rent or buying food.
- Southeast North Carolina has a food insecurity rate of 19%, much higher than the state average of 15.4%.
- Charitable programs are unable to fully support those struggling with hunger. The combination of charity and government assistance programs are necessary to help bridge the meal gap.
The Difference Between a Food Bank and a Food Pantry

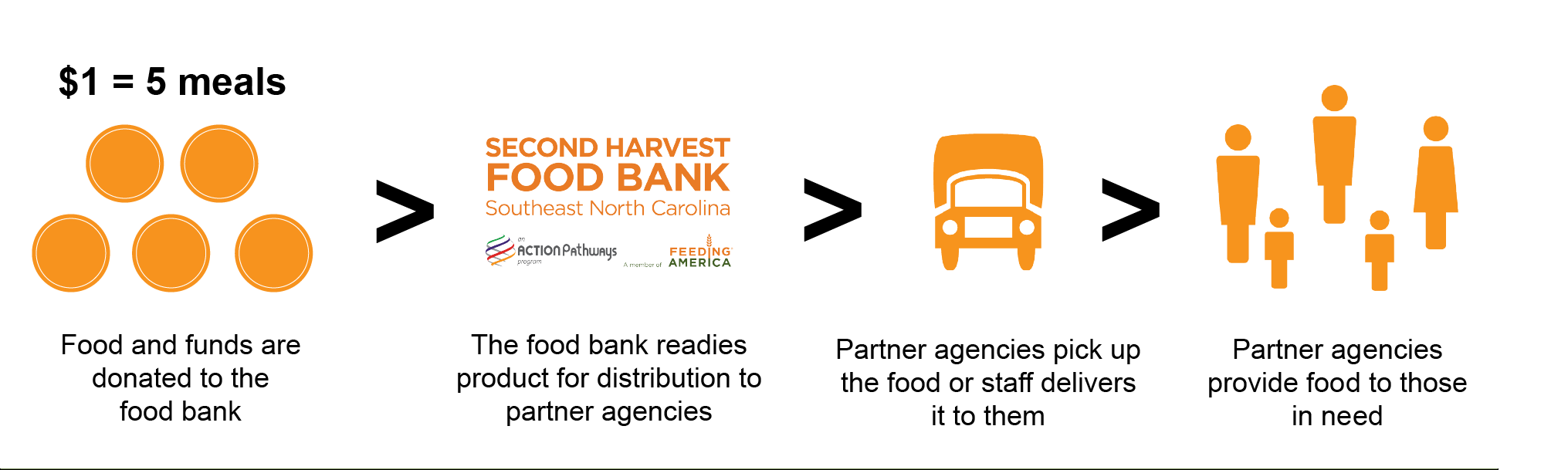
How Do Food Banks Work?
A food bank is a non-profit organization that collects and distributes food to hunger-relief charities. Food banks act as food storage and distribution depots for smaller front line agencies; and usually do not themselves give out food directly to people struggling with hunger.
Food banks in the U.S. are very diverse – from small operations serving people spread out across large rural areas to very large facilities that store and distribute many millions of pounds of food each year, and everything in between. A variety of factors impact how food banks work, from the size of the facility to the number of staff members. But, one thing all food banks have in common is that they rely on donors and volunteers to carry out their day-to-day operations.